If you’re like most people, you probably don’t think about network security very often. But what happens when you do? Do you know how to use the network security tools available to you? Can you keep up with new threats? Are you prepared for the worst?
How secure is your network? Are you sure you are using the latest version of your operating system? Is your router protected against hackers?
Network security has become a major concern for businesses and inspaniduals alike. Hackers are constantly looking for ways to gain access to sensitive information.
It’s important to update your software regularly and ensure that your computer or smartphone runs the latest version. If you don’t, you might be putting your company at risk of cyberattacks.
Understanding the basics of network security is the first step toward building a secure IT infrastructure.
Core fundamentals include:
Students and IT professionals often rely on network security notes to grasp these essential principles clearly.
Network security involves protecting networks from external threats, including unauthorized access, viruses, malware, denial of service attacks, spam, phishing, etc. Regardless of their organization’s scale, type, or infrastructure, Network Security Solution protect them from the always evolving attacks cyber threats. The goal is to keep your network safe from hackers who want to steal information or disrupt operations.
This article will discuss some of the basics of network security, including what it is, why it matters, and how to protect yourself from attacks.
In a digital-first environment, businesses depend on secure communication, cloud platforms, and remote access. This is where network security becomes critical.
The major advantages of network security include:
From startups to global enterprises, effective network security in computer network systems protects operations from disruption.
The most obvious benefit of network security is keeping your company safe from hackers. But it goes beyond that. By securing your network from a wide variety of potential threats, you’re protecting yourself against cybercrime, which includes everything from identity theft to ransomware attacks. And if you want to stay competitive, you’ll need to protect your business’s intellectual property (IP).
Network security can help protect your company’s intellectual property and its internal systems by managing network traffic more effectively, enhancing network performance, and ensuring secure access to sensitive business information.
If you have employees working remotely, they can access files and data stored in your network from anywhere. This means that they could potentially download malicious software onto their computers at home, then bring those files back into your network, where they could compromise your systems. In addition, by not having proper firewall protection, an attacker could gain remote access to your network, allowing them to install malware or spyware that would allow them to view all of your confidential information.
There are many reasons why you should care about network security. You may be concerned about losing sensitive information such as customer records or trade secrets. Or maybe you just don’t like being hacked. Whatever the reason, there are several types of network security that you can protect your network.
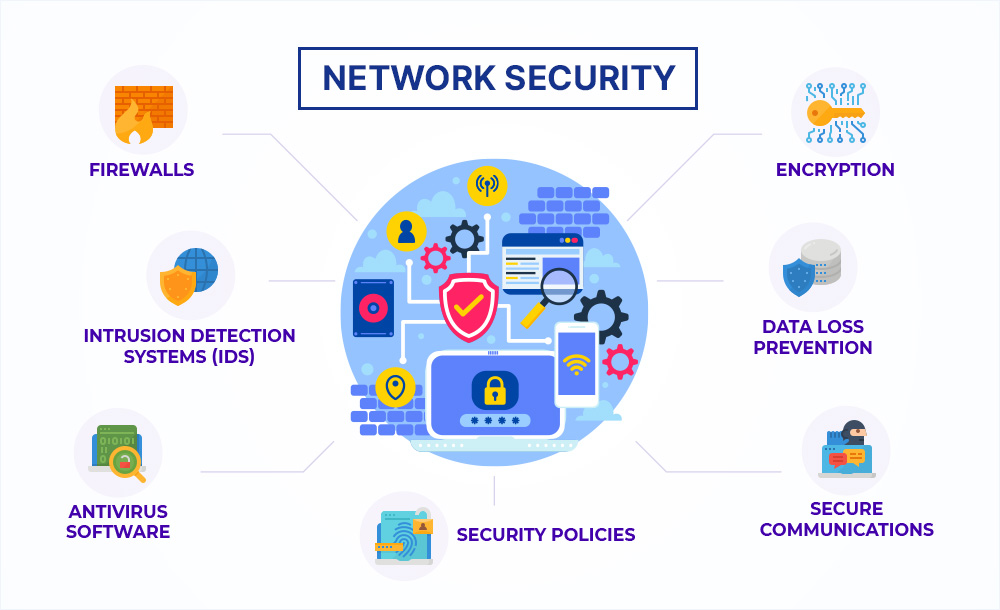
To understand network security in computer network environments, you must know its core components:
These tools represent important types of network security controls used across industries.
Firewalls are designed to prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to your network. They also provide basic filtering for email servers and web servers. If you’re running Windows Server 2012 R2 or later, you can use Microsoft’s Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) feature to help detect and block advanced threats.
An Intrusion Detection service monitors traffic entering and leaving your network and alerts you to malicious activity. Some IDSs can even stop intruders before they get inside your network.
Antivirus software protects your computer from viruses, worms, Trojan horses, spyware, adware, and other types of malware. Most antivirus programs include a firewall, but they aren’t always necessary. For example, Symantec Endpoint Protection provides both virus scanning and firewalling capabilities.
A security policy defines acceptable usage practices for your organization. It helps ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive areas of your network.
Encrypting data ensures that no one can read it without the correct key. Data encryption makes sure that your data is secure even if someone gains access to your network.
Data loss prevention technology prevents sensitive documents, emails and other items from falling into the wrong hands.
Secure communications technologies encrypt messages so that they cannot be intercepted during transmission. These technologies make sure that no one can listen in on conversations or read the private correspondence between people.
Virtual private network encrypts the connections between endpoints and networks, usually over the Internet. A Remote Access VPN typically authenticates communications using either IPSec or SSL.
Segmenting networks by software allows for better enforcement of security policy. Endpoints should be classified by their identities rather than just their IP addresses. You can restrict access by assigning different roles, locations, and permissions for each device, which helps contain suspicious devices and give the right level of access to the correct people.
Industrial network security is an extension of network segmentation, which provides additional visibility into industrial control networks.
Network security requires that both user accounts and device authentication mechanisms be in good shape so that malicious actors cannot gain unauthorized access.
Organizations can strengthen protection by following these steps:
These actions effectively maximize the use of network security practices.
Despite advanced tools, several challenges remain:
Balancing security with usability is one of the biggest hurdles organizations face.
Following proper network security basics is essential for protecting organizations from cyber threats. Implementing strong network security in computer network systems helps reduce vulnerabilities and improve overall system safety.
Below are some important best practices for network security that organizations should follow.
Using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication helps prevent unauthorized access to network resources. Identity verification is a critical component of any modern network protection strategy.
Keeping operating systems, applications, and security software up to date helps eliminate vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit. Regular patch management strengthens the overall security infrastructure.
Continuous network monitoring helps detect suspicious activities early. Security monitoring systems analyze traffic patterns and identify potential threats before they cause serious damage.
Combining multiple security technologies provides stronger protection. Firewalls, encryption tools, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems work together to protect networks effectively.
Employees should understand common cybersecurity risks such as phishing emails and malicious links. Providing clear network security notes and training materials improves awareness and reduces human errors.
Routers, switches, and servers must be properly configured with secure settings. Default credentials should be changed, unused services should be disabled, and encrypted communication should be used whenever possible.
Regular backups ensure that important data can be restored quickly after system failures, cyberattacks, or accidental data loss.
Understanding common threats is critical in any network security wiki resource or learning guide.
Major threats include:
Being aware of these risks helps organizations implement stronger preventive controls.
While both terms are related, they are not identical.
In simple terms, network security is a core part of overall cybersecurity.
Strong security policies define rules for access control, acceptable usage, and incident handling. Compliance ensures organizations meet industry standards and legal regulations.
Without proper governance:
Policies act as the backbone of effective network security basics implementation.
When you connect to a network, you must authenticate yourself with a username and password. The username identifies who you are, while the password verifies that you are who you say you are. Network authentication takes place at two levels:
At the physical level, devices send out signals that identify themselves to each other. Devices that need to communicate with each other establish a connection using these signals. A device might broadcast its presence by sending out radio waves, while another type of device might use infrared light or sound waves.
At the logical level, a user authenticates himself or herself to a system by providing a valid set of credentials. When a user logs on to a network, he or she enters a username and password. This combination of information proves that the person accessing the network is who he or she claims to be.
The most common form of network authentication is known as mutual authentication. In this process, both parties involved verify the identity of the other party. To do this, each party sends an encrypted message containing his or her public key to the other party. Once the recipient has verified the sender’s public key, he or she then decrypts the message using the corresponding private key. Only after verifying the sender’s authenticity will the recipient accept the message.
Authentication methods vary depending on the type of network being used. For example, wireless network often rely on passwords, while wired networks may require usernames and passwords.
There are many different ways that computers can become infected with malicious software. Malicious software includes viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, adware, and other forms of malware. Some of these attacks take advantage of flaws in computer programs or systems. Others attack vulnerabilities in human behavior.
Malicious software can damage or destroy files, corrupt databases, steal personal information such as credit card numbers, and disrupt operations. Even worse, once a computer becomes infected, it can spread the virus to other computers.
Viruses infect programs and data stored on a hard drive. They replicate themselves until all available memory space is filled up. At that point, the program stops functioning.
Worms are pieces of code that copy themselves from one computer to another. Worms can cause problems for their hosts because they consume resources and slow down processing speeds.
Trojan horses are programs designed to look like something else. They disguise themselves as games, music players, or other useful applications. Once installed, they access sensitive information without permission.
Spyware tracks what people do online and reports back to advertisers or others. Spyware also steals personal information such as credit cards and bank account details.
Adware displays unwanted advertisements. These ads appear as pop-up windows or banners. Some adware even installs itself onto your computer without asking for permission.
A hacker gains access to your network through several different means. The most common method involves gaining physical access to the building where your network resides. Hackers may use tools such as lock picks, bolt cutters, or other devices to break into buildings.
Another way hackers get inside your network is via email attachments. Hackers have been known to send out emails that contain links to websites that install harmful software on unsuspecting users’ machines.
Hackers can also exploit weaknesses in your firewalls and routers. A firewall protects against incoming connections by allowing only authorized traffic to pass through. Routers direct packets between two points on a network. If a router fails, it could allow outsiders to connect directly to your internal network.
You should always be careful who you give access to your network. Never share your password with anyone. Make sure that you change your password periodically.
You should also keep your antivirus software updated so that it will detect new types of viruses and remove them before they can harm your system. Antivirus software typically keeps track of which programs you’ve run and compares those programs to known bad ones.
If you receive an attachment in an email message, don’t open it unless you’re certain that you want to see it. Instead, forward the email to someone else to open.
Email security identifies potentially harmful emails and can also be employed to block attacks and stop the spread of sensitive data.
If you suspect that your computer has been compromised, call your ISP immediately. Your ISP can help you determine if there’s malicious software running on your machine.
The best defence against network attacks is prevention. You can reduce the risk of being attacked by following these tips:
Never click on links in unsolicited messages. Always verify that you trust the sender before opening any attachments.
Do not download files from untrusted sources. Use trusted sites such as Google, Yahoo!, and Microsoft.com.
Be wary of suspicious emails. Check the return address before opening an email. If the email comes from an unknown source, delete it immediately.
Be cautious when browsing the web. Avoid clicking on links in unsolicited emails. Look for signs of phishing scams.
Use strong passwords. Create unique passwords for each site. Don’t reuse passwords across multiple accounts.
Use a firewall. Firewalls are designed to block unwanted traffic. They can help protect your computer from malware.
Update your antivirus software regularly. This will ensure that your antivirus program detects and removes all types of viruses.
Keep your operating systems up to date. New versions of Windows and Mac OS X come out frequently. These updates often include fixes for security holes.
Don’t forget to update your firmware. Firmware is the code that controls hardware functions like disk drives and printers. Updating this code ensures that your device works properly.
Don’t use public wireless networks. Public wireless security networks may be vulnerable to eavesdropping or hacking.
There are many ways to attack your network. The most common way is through the Internet. Hackers can gain access to your network through a number of different means. For example, they might use a Trojan horse (malicious software) to get into your network. Or they might try to break into your network using social engineering techniques.
Social engineering involves tricking people into giving away their login credentials. Once hackers have gained access to your network, they could install spyware or other forms of malware. Spyware monitors what users do on their computers. Malware does things like steal personal information or causes damage to your computer.
Another way to attack your network is via physical access. Someone who gains physical access to your building could plug a laptop directly into your network without your knowledge. As long as they know how to bypass your router’s password, they could potentially security control your entire network.
Finally, attackers could exploit network vulnerabilities in your mobile devices. A vulnerability is something that lets hackers take advantage of a weakness in your system.
Network security is very important because it protects your business from threats. Network security helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing your network. It also prevents them from stealing data or causing harm to your network.
The most common types of attacks include viruses, worms, spyware, spam, denial of service (DoS) attacks, and hacking. Hackers can gain access to your computer by breaking into your system through any of these methods. They may then steal information, damage files, or shut down your computer.
In conclusion, there are many ways to attack a network. However, effective network security is one of the best defences against such attacks. By following some basic guidelines, you can keep your network safe.
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping modern security strategies. AI-powered systems can:
Emerging trends include:
These innovations enhance the overall advantages of network security by improving accuracy and response time.