Editor’s Note: This article defines cyber incidents as events that threaten the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of digital assets—ranging from malware infections to unauthorized access. It highlights the... Read More
Cyber incidents are becoming more common these days. The term “cybercrime” was coined in 1989, and since then, it has become a significant concern for both individuals and organizations. Cybercrimes include hacking, phishing, malware, ransomware, spam, identity theft, data breaches, and other malicious activities.
A cyber incident occurs when someone uses information or resources belonging to another person without permission. These incidents can happen at home, school, or work, and they can also involve personal devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and even smart TVs.
This article explains what a cyber incident is and how it affects your business. We also cover some of the most common types of cyber incidents that you might face.
A cyber incident is defined as “a deliberate attempt to gain unauthorized access to computer systems to disrupt normal operations, steal information, or destroy data.” It could involve stealing money, credit card numbers, passwords, or other sensitive information. It may also damage the organization’s reputation or cause a loss of business.
A cyber incident could take many forms. It might involve a hack into a company website, where sensitive information is stolen, and it could involve a phishing email that tricks users into giving away personal details.
It could involve malware infecting a computer system, which then starts sending out spam emails, or it could include hackers using denial of service (DoS) attacks against a particular website, making it unavailable to its intended audience.
If a cyber incident happens on your network, it can have severe consequences for your business. The following sections describe some of the effects of cyber incidents on your business.
Hackers often use cyber incidents to steal money from people’s bank accounts. For example, if a hacker gains access to your online banking account, they will be able to transfer funds out of your account. If your employer doesn’t reimburse you for the lost income, you’ll likely need to pay the amount yourself.
A cyber incident can make your customers think less highly of your brand, resulting in fewer sales, lower profits, and increased costs.
If you’re involved in a cyber incident, you could be held liable for damages caused by your employees or contractors. You could be sued for negligence, breach of contract, or failure to provide adequate security.
Your business continuity plan should address all aspects of a cyber incident. In addition to addressing financial losses, it should help prevent further damage to your company’s reputation.
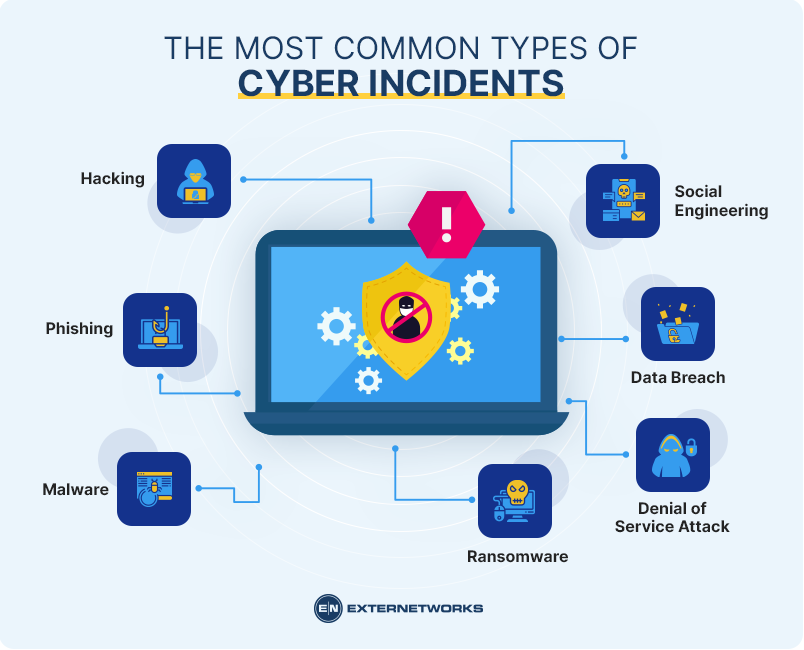
Hacking – An unauthorized attempt to access the computer system by using software tools such as viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, keyloggers, rootkits, etc.
Phishing – A fraudulent email message sent to trick users into revealing personal information like usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, bank account details, social security numbers, etc.
Malware – Malicious code designed to damage computers or steal sensitive information. It can be embedded in various electronic messages (like spam) or downloaded from websites.
Ransomware – Software used to encrypt files on your computer and demand money for their return. This includes programs like Cryptolocker, Locky, WannaCry, NotPetya, etc.
Denial of Service Attack – A type of attack where hackers use large amounts of computing power to make a website inaccessible or slow down its performance.
Data Breach – When confidential information about individuals is stolen. This could include names, addresses, Social Security Numbers, phone numbers, financial records, medical records, etc.
Social Engineering – Using human psychology against people to gain access to confidential information. For example, someone might call you pretending to be a company representative asking for your password.
If you suspect that your organization has been hacked, there are several ways to determine whether this is true. You may have already noticed signs of intrusion, but they may not be conclusive. There are also some simple steps you can take to protect yourself. Here are some things to consider:
Check your firewall logs – Look for unusual activity on your network. If you see anything suspicious, contact your IT support team immediately.
Once you realize your organization has been compromised, you need to act fast. Your first step should be to contact your IT support team so they can investigate what happened. After that, you need to decide how to handle the situation.
Organizations need to prepare for a cyber incident. The first step is to understand the potential impact of such an event. What financial damage can it cause? How long will it be a problem? Will reputational damage affect your organization?
Once you have assessed the risk, you should develop a strategy to deal with it. You should consider whether to prevent the attack from happening, detect it as soon as possible, or both.
Once you have identified the risks posed by a cyber incident, you can start mitigating them. For example, you could use firewalls to block unauthorized traffic entering your network and encrypt sensitive files on your computers and servers.
If you have been affected by a cyber incident, here are some tips to help you recover:
Get advice from experts – seek help from people who have experience dealing with similar situations.
Document everything – record all conversations and actions taken during the incident.
Keep calm – don’t panic. Take deep breaths and try not to think about what happened.
Don’t make assumptions – gather evidence to support your claims.
Be honest – tell the truth when asked questions.
Talk to others – share your experiences with trusted colleagues and friends.
Seek legal advice – find out if you have a duty of care towards your customers or clients.
There are several ways to prevent cyber incidents. The first step is to educate yourself about cybersecurity. Things to consider to avoid cyber incidents :
Cybersecurity is a complex topic, and it involves many different areas of expertise, including information technology, law, business management, psychology, ethics, and more. However, there are things you can do to reduce the impact of cybercrime. By taking simple precautions, you can minimize the risk of a cyber incident occurring.
At ExterNetworks, we understand the importance of staying one step ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. With our proactive monitoring services, you can rest easy knowing that potential threats are being identified and addressed before they can impact your organization. Our team of cybersecurity experts brings years of experience to the table, ensuring that your systems are always protected against the latest threats.
We offer customized solutions to fit your unique cybersecurity needs, ensuring you receive the level of protection your organization requires. Additionally, we help keep your organization compliant with industry regulations and standards, giving you peace of mind knowing that your data is secure.
By choosing ExterNetworks for cyber threat monitoring services, you can save on the costs of hiring an in-house security team while benefiting from top-notch protection. Don’t wait until it’s too late—contact ExterNetworks today to learn more about how our services can benefit your organization.